MSS Clamping
Introduction
MSS is the maximum payload size a TCP connection agrees to send, so packets don't get broken up in transit.
When traffic reaches via Cloudflare Magic Transit, the effective path MTU is smaller than standard Ethernet.
If TCP peers advertise the default MSS of 1460, larger packets on that path can get dropped or fragmented,
causing:
- flaky HTTP(S)
- slow downloads
- stalls or resets
The fix is to clamp TCP MSS of IPv4 to 1436 on SYN at an operating-system level.
Diagnosing
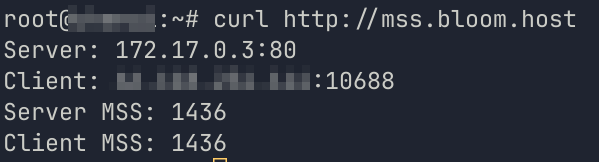
To determine your current MSS, simply make an HTTP (not HTTPS) request to http://mss.bloom.host using your
favourite client, such as curl or wget for Linux and Invoke-WebRequest for Windows.
The resulting Client MSS should be 1436 or lower. Otherwise, make sure to follow the steps below to change it.
Here's an example:
Using TCPDump (Alternative)
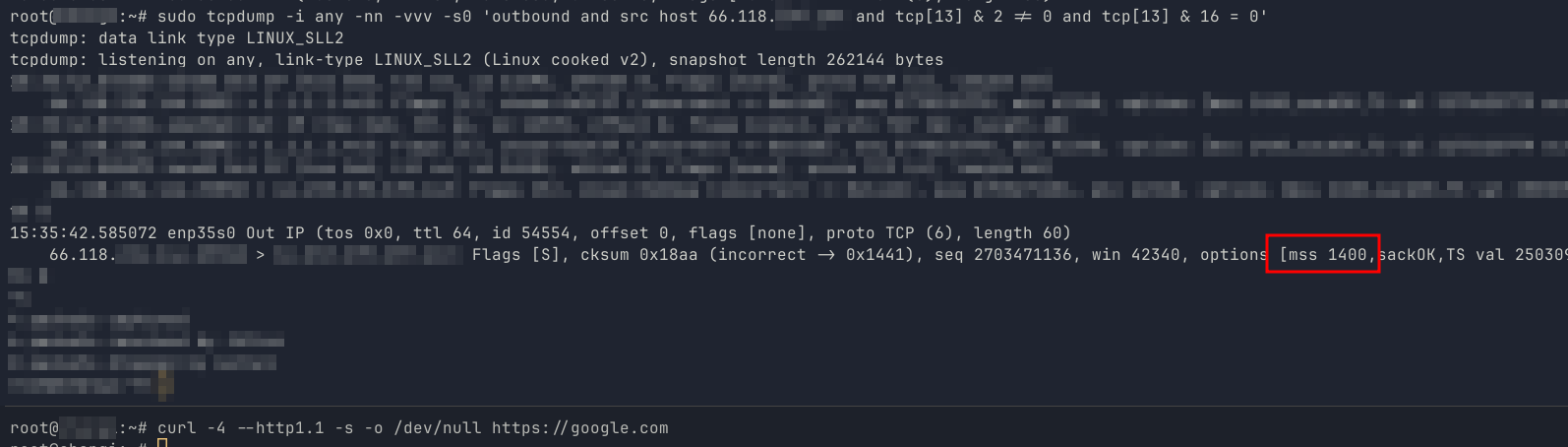
To confirm your current MSS, you can use TCPDump to listen to the traffic.
Make sure to replace <server IP here> with your server's public IPv4 address.
sudo tcpdump -i any -nn -vvv -s0 'outbound and src host <server IP here> and tcp[13] & 2 != 0 and tcp[13] & 16 = 0'
While that's running, execute a simple HTTP request from the machine in another terminal:
curl -4 --http1.1 -s -o /dev/null https://google.com
Stop TCPDump with CTRL+C and above, you should see something like this:
Flags [S], ... options [mss 1400,sackOK,TS,...]
Setting Up Clamping
All of our standard Bare Metal installations have MSS clamping enabled by default; however, if you are installing your operating system manually, you'll need to make sure to set this up.
Click on the section to expand it.

Linux

Each distribution has its own way to set this up, but here are some common ones.
In either case, make sure to check the new MSS value after the adjustment using the diagnostic step to confirm it worked.
IPTables (Debian, Ubuntu, etc)
If you use iptables, you can use the following command to set the MSS:
iptables -t mangle -A POSTROUTING -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1436
To make sure it's applied after a reboot, you can do the following to add it to crontab:
(crontab -l ; echo "@reboot /sbin/iptables -t mangle -A POSTROUTING -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1436 >> /dev/null 2>&1")| sudo crontab -
firewalld (RHEL, CentOS, Rocky Linux, Alma Linux, Fedora, etc)
When using firewalld, you can use the following command to set the MSS:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule tcp-mss-clamp value=1436'
firewall-cmd --reload
Automatically
If you're unsure about your setup specifics, you can also use our script, which will automatically
attempt to create the necessary rule for you using nftables
We have tested this on the following distributions:
- Debian 13, 12, 11
- Rocky Linux 9, 10
- Alma Linux 8, 9, 10
- Oracle Linux 8, 9
- Proxmox VE 8, 9
- Ubuntu 20, 24
curl -s https://bloom.host/scripts/mss-clamping.sh | sudo bash

Windows

Unfortunately, Windows does not support MSS clamping via the built-in firewall or netsh. Instead, you'll need to set the interface MTU instead. MSS will follow from MTU. For IPv4, MSS = MTU - 40. In our case, setting MTU to 1476 will ensure MSS will match the required 1436.
To do this, open a new PowerShell window as Administrator.
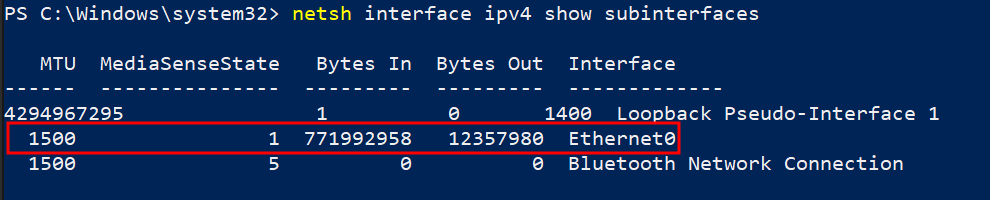
Check the name of the active interface, usually something like Ethernet0:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
Using the interface name, set the MTU to 1476:
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface "<your interface here>" mtu=1476 store=persistent
As an example, you can see Ethernet0 is set to 1500 currently:
We will use the following command to update it:
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface "Ethernet0" mtu=1476 store=persistent
You can re-run the original command and also check the new MSS value using the diagnostic step to confirm it worked.
Troubleshooting
If you run into any issues, please contact us.